| 公司: | GVL怡境国际设计集团 | 类型: | 景观 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 地区: | 中国 | 标签: | 海绵城市 | 公园绿地 |
导言
10月4日,美国风景园林师协会专业奖(ASLA Professional Awards)公布了2021年获奖名单。GVL怡境国际设计集团的《低成本-高效能:运用低影响开发设施构建偏远地区生态污水处理系统》(Low-cost and High-efficiency: Use Low-Impact Development Facilities to Build an Ecological Sewage Treatment System for Remote Areas)夺得研究类(Research Category)荣誉奖(Honor Award)。
Introduction
On October 4, the American Society of Landscape Architects (ASLA) announced the winners of the 2021 ASLA Professional Awards. GVL’s “Low-cost and High-efficiency: Use Low-Impact Development Facilities to Build an Ecological Sewage Treatment System for Remote Areas” won the Honor Award of Research Category.
怡境设计21年来重视生态建设,对海绵技术有持续的研究,并一直在项目中探寻着技术与景观的结合。获奖课题是GVL怡境国际设计集团研究中心设计总监闾邱杰带领团队对广东省清远飞来峡水利试验基地内一个中心湖区改造成果。该项目不仅运用了海绵技术,同时与景观改造达到很好的结合,更重要的意义在于,它为那些地理位置偏远和资金缺乏地区的生活污水排放问题提供了一种“低成本,高效能”的解决方案。
Over the past 21 years, GVL keep putting its effort in sustainable practice and technical research on Sponge City, trying to integrate the technology with landscape in each practice. This award-winning project is located in the central lake and surrounding area of Feilaixia Water Conservancy Hub, in Qingyuan city, north of Guangdong. which was led by Lvqiu Jie, the design director of GVL, has successfully integrated the Sponge City technology with landscape design. More importantly, it provides a "low-cost, high-efficiency" solution to the domestic sewage discharge problem in areas with remote locations and lack of funds.
本篇专题,我们邀请到闾邱杰团队为本栏独家撰稿,为大家解读飞来峡海绵公园技术。
This article, contributed by Lvqiu Jie Team, will in-depth introduce the technology applied in Feilaixia Sponge Park.
跟主创设计师闾邱杰一起认识飞来峡海绵公园
Let’s learn more about Feilaixia Sponge Park together with the chief designer, Mr. Lvqiu Jie.
研究背景 Research Background
飞来峡海绵公园是广东省水利试验基地(以下简称“基地”)内一个中心湖区的改造项目,它的地理位置处于城市基础设施较为薄弱的区域,周边没有污水处理厂。
Feilaixia Sponge Park is located in the central lake area of Guangdong Water Conservancy Hub (hereinafter referred to as “hub”), which is remote with under-developed municipal infrastructure and without sewage treatment facilities around.
那么,基地的科研人员和管理人员的生活污水只能采用简单的二级化粪池处理后直接排入中心湖,导致中心湖水质逐年恶化。改造前湖水的水质为劣五类,水生态系统遭受破坏,周边的人居环境也相对糟糕。
As a result, the sewage from the research zone, office and living area on the site have been only treated with basic secondary septic tanks, and directly discharged into the pond of the park. The water quality of the pond has deteriorated year by year, which does not even meet the requirement for agricultural irrigation prior to the works. Meanwhile, the renovation was restricted due to a shortage of funds, which result in serious damage to the environment and biodiversity of the pond and surroundings.
因此基地亟需开发廉价、便捷的污水处理技术,解决基地的日常废污水排放问题,并对心湖的生态环境进行修复,恢复心湖的水质和生态系统。
Therefore, a low-cost and high-efficiency sewage treatment system is urgently needed to properly discharge the sewage, improve the surrounding environment, and enhance the water quality and restore the ecological system as well.
同时,使用者对提升园区的人居环境和生态环境抱有极大的期待,兼顾雨、污水处理功能和景观功能,打造宜人、宜居、宜水的多功能生态公园,实现低维护、低成本运营。
Moreover, users of the hub are seeking to a comfortable and ecological environment with low maintenance cost and high operational efficiency to solve both sewage treatment and stormwater management issues.
▲严峻的生活污水排放形势 Severe situation of domestic sewage discharge
▲生活污水的组成 Cause and composition of domestic sewage
▲生活污水带来的危害 Domestic sewage threatens human well-beings
▲地理位置偏远和资金缺乏导致基地的生活污水排放问题一直无法得到妥善解决
Domestic sewage treatment in remote area was restricted due to its location and shortage of funds.
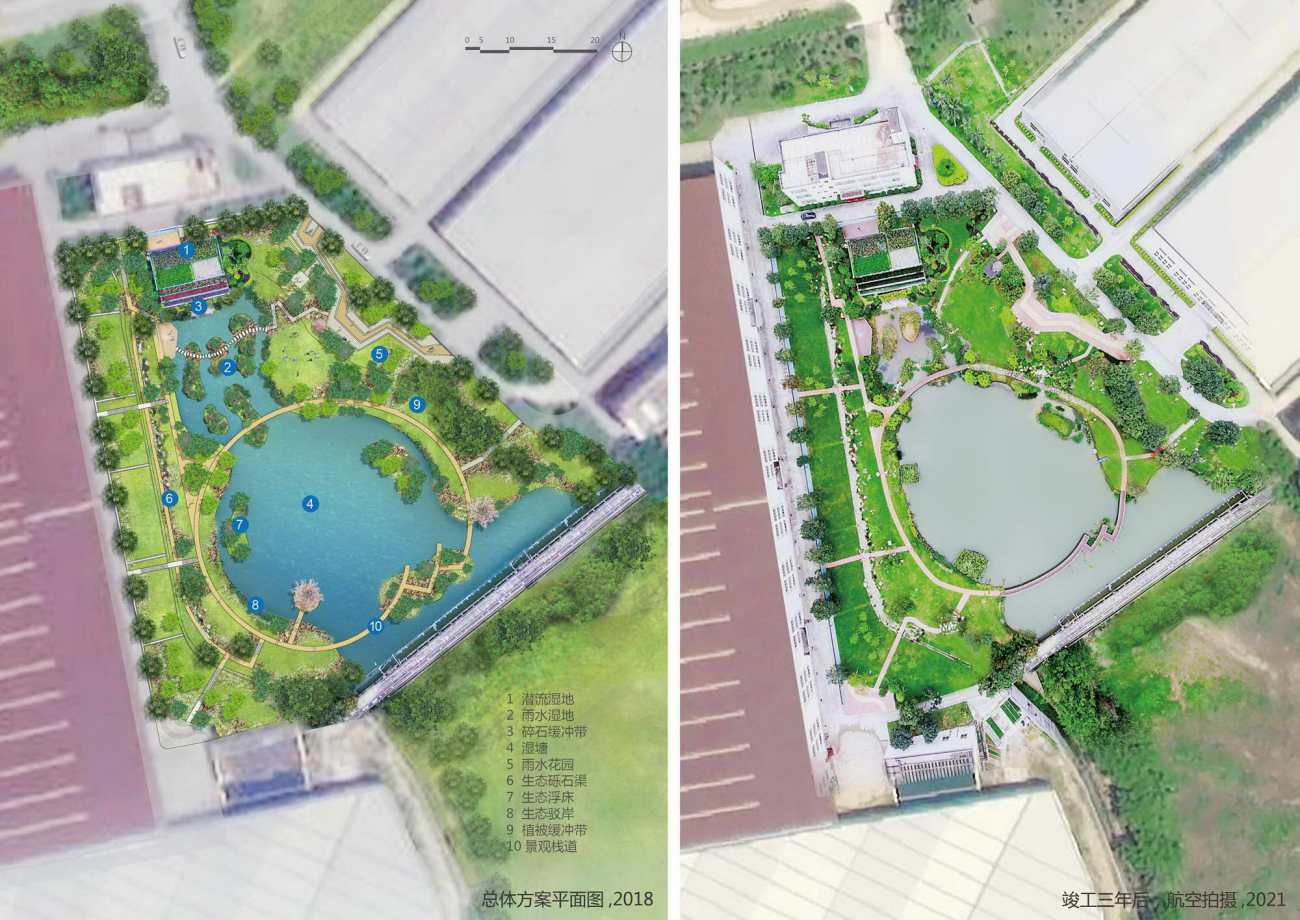
▲总平面图与建成后的卫星图 Overall masterplan and satellite image after completion
▲从设计到实施,项目已经建成三年,水质逐渐提升,植被和环境逐步恢复,为园区的工作人员提供了舒适的办公环境
The project was completed in 2018 and has been in operation for three years. Now the quality of water has been gradually improved, and the plants and environment have been restored, which provides a pleasant working environment for the staff of the hub.
猜想与研究 Assumption and Research
基于此背景,我们与华南理工大学联合组成课题研究小组,不同于以往传统的工程项目是以经验视角开展设计,我们是以科研视角为切入点,提出以“低维护成本,高运转效率”的景观策略取代成本高昂的传统工程的设想,并将其拆解为以下2个子问题进行了探讨:
Based on the research objective, we teamed up with South China University of Technology (SCUT) and made an assumption that will replace the high-cost traditional engineering methods and used landscape strategies with "low maintenance cost and high operational efficiency" to solve the sewage treatment problems. The project aims to address:
(1)景观策略中所包含的处理污水的低影响开发设施手段有哪些?这些低影响开发设施手段能否同时作用于雨水带来的地表水污染,以及生活污水的处理?
(1) What are the effective Low Impact Development (LID) facilities for sewage treatment? Can these approaches simultaneously act on the treatment of the surface water pollution caused by rainwater and domestic sewage?
(2)如何在低成本的制约下,有效地组合不同类型的低影响开发设施(包括类型、各类的占比)使其发挥最优的净化效果,达到“低成本,高效能”的目的?
(2) How to effectively combine different types and proportions of Low Impact Development (LID) facilities under low cost constraints to achieve the optimal purification performance and achieve the goal of “Low cost and High efficiency”?
基于上述问题,我们提出了三个研究计划:
Based on the questions above, we came up with three research plans:
1.将LID设施、植物和基质作为构建低成本高效生态污水处理系统的三大核心要素。
1.Focus on Low Impact Development (LID) facilities, plants and substrates to build a low-cost and high-efficiency sewage treatment system.
2.从净化效率、建设和维护成本三个维度选择最佳系统组合模式。
2.Choose combinations in terms of construction cost, maintenance cost and the plant’s purification performance.
3.除污水处理外,还应从审美价值、教育价值、社会价值等多个维度构建可持续的生态景观系统。
3.Establish a sustainable landscape system from the perspectives of aesthetics, education and social influence.
▲LID设施、土壤和基质的选择与组合方式是解决问题的关键
Combination of LID facilities, soil and substrates is the key to solve problems.
我们与污水处理专家、植物学专家以及水利工程专家建立合作,通过田野调查、适应性建模(SWMM)、正交试验等研究方法,从建造成本、维护成本、基质与植物对污水的净化能力等方面,定量分析并比对不同低影响开发设施组合的成本和效能,最终获得了最佳的低影响开发设施的组合方式与配比,即当潜流湿地、表流湿地、湿塘、生态浮床4种低影响开发设施分别占比4.76%,15.87%,71.43%以及7.94%的时候,对于该基地而言,污水处理策略具有最优的效能。
We collaborated with specialists in the fields of sewage treatment, phytology and water conservancy engineering, and built models through field study, adaptive modeling Storm Water Management Model (SWMM) and orthogonal experiments, to quantitatively analyze and compare the wastewater treatment strategies of different Low Impact Development (LID) facility combinations in terms of construction cost, maintenance cost, substrate and the plant’s purification performance. When the four types of LID facilities including constructed wetland, rainwater wetland, wet pond and artificial floating islands, account for 4.76%, 15.87%, 71.43% and 7.94% respectively, the sewage treatment strategy has the optimal efficiency on the site.
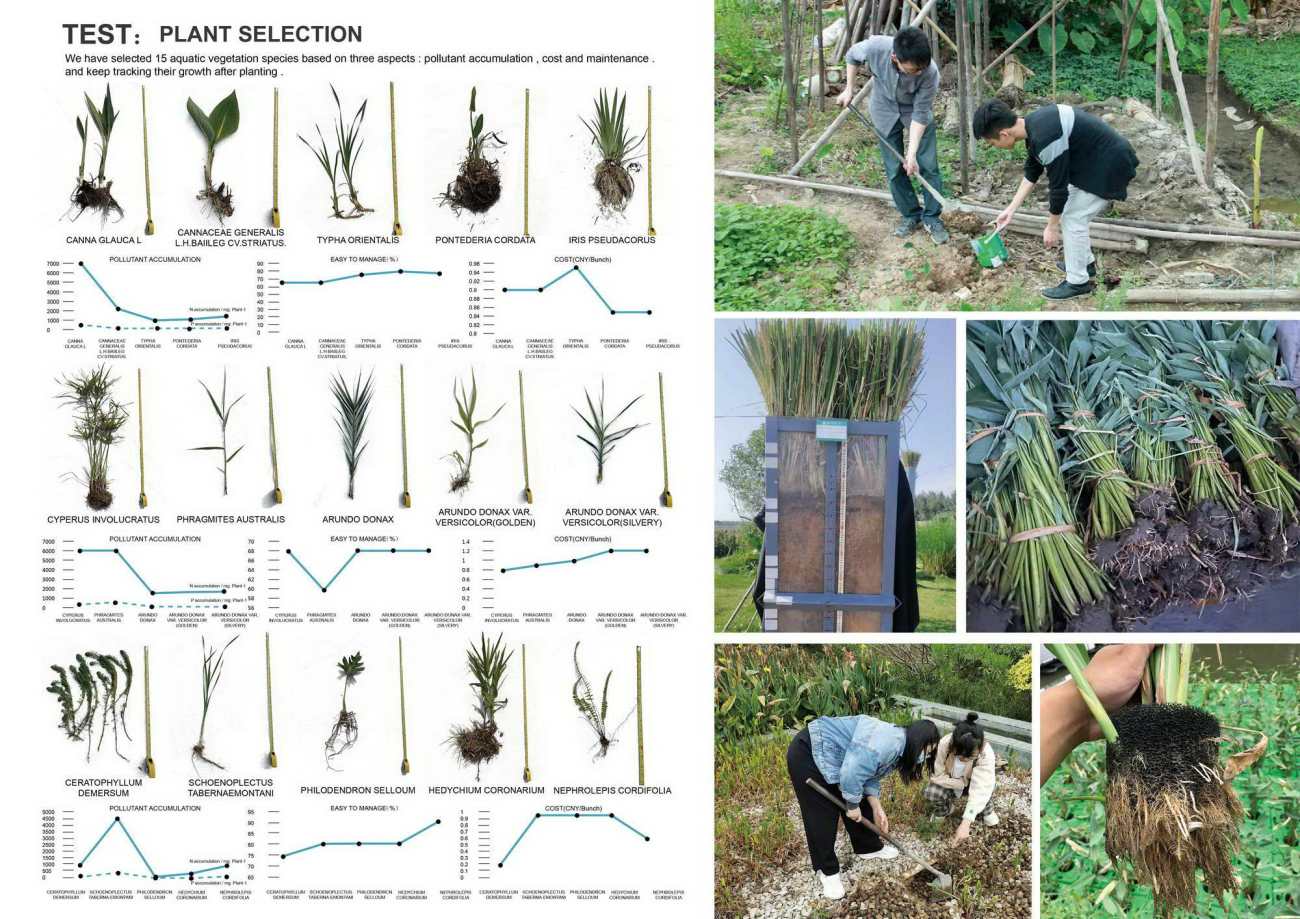
▲研究过程:植物的筛选与生长状况跟踪
TEST: Plant selection and tracking of their growth
▲研究过程:基质的筛选与跟踪
TEST: Substrates selection and tracking
▲研究过程:通过SWMM模拟分析潜流湿地、表流湿地、湿塘、生态浮床对污染物处理效率,叠加分析每个设施的建设与维护成本,所能作用的规模,以及使用寿命。
METHOD: The runoff control rate, the removal rate of TSS (total suspended solids) and TP (total P) are simulated respectively on the SWMM platform, and the calculation of construction and maintenance costs are superimposed to determine the optimal combination mode to achieve Low-cost and High-efficiency.
▲研究过程:根据正交试验法则,将四个低影响开发设施作为组合因子,模拟出9种组合方式,在SWMM平台中分别模拟径流控制率,TSS和TP的去除率,并叠加建造及维护成本的计算,最终确定低成本高效能的最优组合方式。
METHOD: According to the principle of the orthogonal experiment, four LID facilities are used as combination factors, based on which nine types of combinations will be simulated. The runoff control rate, the removal rate of TSS (total suspended solids) and TP (total P) were simulated respectively on the SWMM platform, and the calculation of construction and maintenance costs are superimposed to determine the optimal combination mode to achieve Low-cost and High-efficiency.
▲研究结果:潜流湿地、表流湿地、湿塘、生态浮床4种低影响开发设施分别占比4.76%,15.87%,71.43%以及7.94%的时候,对于该基地而言,污水处理策略具有最优的效能。
Research Result: When the four LID facilities of constructed wetland, rainwater wetland, wet pond and artificial floating islands account for 4.76%, 15.87%, 71.43% and 7.94% respectively, the sewage treatment strategy has the optimal efficiency on the site.
▲建成后的基地景观更加趋于原生态,除了必要的维护,几乎不需要人为介入,这正符合我们对该场地的预期效果。
After completion, the landscape here is in a natural state and runs effectively without any human intervention except necessary maintenance, which nicely achieves our expectation.
设计策略 Design Strategies
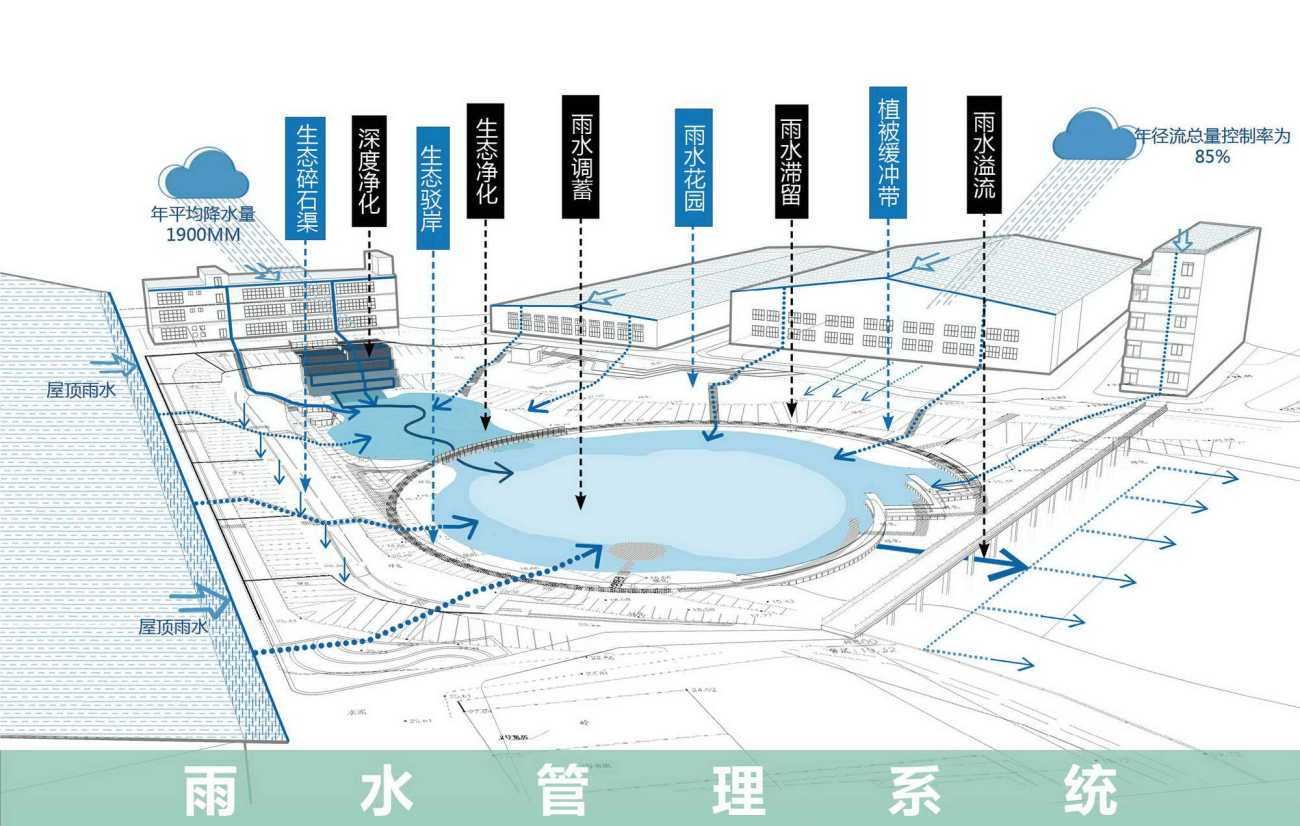
基于以上研究结果,我们首先在场地中设计了两个系统,分别是污水管理系统和雨水管理系统。
Based on the research conclusions, we first laid out two system on the site, respectively the sewage treatment system and the rainwater treatment system.
这两个系统是相辅相成的耦合关系,雨水可以进入污水系统中参与水质的净化,污水处理后则可以作为补充水源进入雨水管理系统中,由二者共同作用,构建健康的生态系统。
These two systems are complementary and coupled. Rainwater can enter the sewage system to participate in the purification of water quality, and after sewage treatment, it can be used as a supplementary water source into the rainwater management system. The two work together to build a healthy ecosystem.
▲建成后的全貌 overall view
为了最大化地发挥低影响开发设施在场地中的作用,我们在现有研究结果的基础上,针对基地所具有的特质,提出了2个创新性的设计策略:
In order to maximize the capacity of LID facilities on the site, the research team proposes two innovative design strategies which match with site characteristics based on the result of the research.
1.针对场地高差大的问题,将潜流湿地的设计结合场地高程进行改造,将潜流湿地改造为台地形式,一方面消化基地内8米的高差,另一方面最大限度地扩大水体面积,使得湿地的去污效能与景观展示功能都发挥到最优。
1. To resolve the huge difference of elevation on site, the constructed wetland was designed as terraces. On the one hand, it resolves the height difference of 8 meters of the site, on the other hand, it maximizes the water body area, so as to maximize the decontamination efficiency, at the same time, it can also provide more potential for landscape opportunities.
▲台地形式的人工湿地水处理流动路径
Constructed wetland is designed as terraces for efficient water treatment
▲表流湿地承接来自潜流湿地的雨水和污水尾水进行二次净化
Secondary purification of waste water and rainwater from subsurface wetland
2.创新性地改变填料在潜流湿地中传统的横向布局方式,采用竖向布局,增加潜流湿地与污水的接触面积,提升净化效率。
2. To increase the contact area between the constructed wetland and the sewage, we introduced a brand-new vertical layout for substrates instead of the traditional horizontal layout, which proved higher efficiency in decontamination.
▲创新的填料布局方式提升污水净化效率
A brand-new vertical layout for substrates is introduced to achieve higher efficiency in decontamination.
研究与设计落地 Implementation of the research and design
为了提升基地内的人居环境,增加舒适的休闲娱乐体验,我们还在园区内做了许多景观化和艺术化的改造和设计,其中包括:
To improve the living environment and upgrade the recreational experience, we introduced some landscape and artistic renovation and design, including:
▲生态碎石渠内的碎石取自本地采石场,形成的景观效果与本地的水文风貌相互呼应
Gravel from local quarry used in ditch for both drainage and decoration purpose
▲利用建筑废弃材料制成的透水铺装补充吸纳两侧绿地产生的雨水径流
Permeable pavement made of recycle waste building materials collects runoff from the green land.
▲外部雨水排水口的生态化设计
Ecological design of external rainwater outlet
▲亲水栈桥与湿地相互呼应,带来舒适的游览体验
The boardwalk dialogues with the wetland and provides a comfortable sightseeing experience.
▲湿地内净化的雨水经过低堰步道跌入湿塘中
The purified rainwater in the wetland falls into the wet pond through the low weir trail
▲生态浮床 Artificial floating island
▲雨水花园 Rainwater garden
▲科普走廊:设计师根据海绵系统规划园区内的动线,完整地向社会人士、校园学生、专业同行展示了从收集传输到储存净化的雨水管理全过程,具有极佳的教育意义。
Science popularization passage: a sponge system visiting tour route was carefully planned, showing the whole process of stormwater treatment to the visitors.
▲由多种乡土植物组合配置形成的景观花镜
garden decorated by a variety of selected local plants
A landscape flower border formed by a combination of a variety of native plants
结语 Conclusion
飞来峡海绵公园以250/㎡的建造成本,解决了该场地的污水处理问题,相比传统的工程手段节省了近40%成本。同时将原本生态恶劣的污水塘及其周围环境,改变成集休憩、观赏、生态功能为一体的办公休闲绿地,实现了以“低成本-高效能”的景观策略解决偏远地区污水处理的问题。
The research project solved the sewage treatment problem of the site with a relatively low construction cost of CNY¥250/㎡, saving nearly 40% of cost compared to traditional engineering methods. At the same time, the original poor ecological sewage pond and its surrounding environment is transformed into a picturesque landscape garden and eco-friendly habitat. This research project demonstrates a “low-cost-high-efficiency" landscape strategy to solve the problem of sewage treatment in remote areas.
鉴于此,该项目已作为水生态技术示范区被推广,获得了社会各界的参观与关注,具有科普、教育的作用,帮助提升公众的生态意识。更重要的是,本项研究从分析方法到技术手段,都具有极高的可复制性,能够为世界各地遭受生活污水困扰的地区贡献具有普适性的解决路径,从而改善经济落后的偏远地区的生存环境。
The project has been promoted as a water ecological technology demonstration area and has received visits and attention from all over the country. It plays a role in science popularization and helps to raise the public ecological awareness. More importantly, this research is highly replicable and provides a universal solution for areas suffering from sewage issues all over the world, helping to improve basic living conditions in undeveloped and remote areas.
合作机构 Partners
海绵城市:华南理工大学建筑学院风景园林系
水生态技术:广东省水利水电科学研究院
施工单位:广州市华慧园林工程有限公司
Sponge city consultant: Department of Landscape Architecture, School of Architecture, South China University of Technology
Water treatment technology: Guangdong Research Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower
Construction: Guangzhou Huahui Landscape Engineering Co.,Ltd.
更新日期:2021-10-22 18:05:54
非常感谢 GVL怡境国际设计集团 带来的精彩项目, 查阅更多Appreciations towards GVLlandscape for sharing wonderful work on hhlloo. Click to see more works!